Casting/en: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
# Place the required mold to be filled on a solid surface. Tool molds occupy one block while ingot molds may be placed two to a block. | # Place the required mold to be filled on a solid surface. Tool molds occupy one block while ingot molds may be placed two to a block. | ||
# With the glowing crucible in an empty hand (active hotbar slot) and a pair of {{ll|tongs|tongs}} in your off-hand, select the desired mold with the display crosshairs and pour the liquid metal into that mold. | # With the glowing crucible in an empty hand (active hotbar slot) and a pair of {{ll|tongs|tongs}} in your {{ll|off-hand|off-hand}}, select the desired mold with the display crosshairs and pour the liquid metal into that mold. | ||
# When the mold is filled, metal will no longer be allowed to be added into the mold. | # When the mold is filled, metal will no longer be allowed to be added into the mold. | ||
# The metal will reach various states of cooling in the mold- from liquid to soft to hardened to cold - which can be identified with the current item temperature in the mold GUI. | # The metal will reach various states of cooling in the mold- from liquid to soft to hardened to cold - which can be identified with the current item temperature in the mold GUI. | ||
Latest revision as of 06:43, 20 August 2023

This page is outdated.
The content on this page is not up to date with the most recent game update. If you do wish to contribute, please request wiki edit access on the Discord.
Casting is the process of smelting ore into a liquid state and molding the molten metal into quick and convenient tool heads and ingots. While not inherently the most important facet of metallurgy, it is one of the first gateways by which a seraph can forge ahead into the throes of advancement and survival.
Required Materials
To cast metal, a player needs a crucible and molds, a firepit, fuel (firewood, peat, coal, charcoal, or coke), and ore nuggets. Players can also use metal bits as an alternate source of metal, obtained by combining a metal tool head or an ingot with a chisel in the crafting grid.
Whereas most ore nuggets can be thrown within the crucible and cast, because of high temperature thresholds and a lack of fuels that reach those thresholds, Iron, Meteoric Iron, Blister Steel, and Steel must be bloomed, smithed on an anvil, or carburized in order to be utilized.
Obtaining metal
Ore nuggets can be found in one of four ways: panning, cracked ore vessels, buying them directly from a trader, or via surface ore bits.
- Panning sand, gravel, or bony soil can yield a 15% chance or less to receive copper, gold, silver or tin nuggets, which can be good in a pinch.
- Cracked ore vessels contain a small assortment of bismuth, chromium, copper, gold, lead, silver, tin, titanium, and zinc nuggets; these vessels can be found in surface or underground ruins or sold by Treasure Hunter traders.
- Commodities traders might have bismuth, copper, tin, and zinc nuggets circulating in their current goods rotation.
- Surface ore bits can be found in most rock types, with the exception of bauxite, halite, obsidian, scoria volcanic rock, suevite impact rock, and tuff volcanic rock. These ore bits contain a single nugget that can be collected by breaking the stone with an empty or filled hand (active hotbar slot), and are an indicator of larger underground deposits.
- Depending on the ore and stone combination, they can blend into the environment and be easily missed.
- While suevite impact rock is by itself not a host rock for ore, its presence is an indicator of meteoric iron.
It is recommended to add waypoints to any ore location for later collection operations, especially with regards to a full inventory or a current lack of need for that particular ore.
An alternate source of metal comes from metal bits, which can be obtained by combining a chisel with any metal tool head or ingot in the crafting grid. This allows players to break down metal items and re-cast them for other uses.
Preparing metal
While loose nuggets are ready to be smelted and do not require additional preparation, the nuggets within regular and crystallized chunks are trapped within their parent stone, such as basalt or kimberlite, and are otherwise unusable until they are further processed. Chunks are placed in the inventory crafting grid under any tier of hammer, which crushes the stone and extracts the nuggets inside.
There are four kinds of ore chunks - poor, medium, rich, and bountiful.
- Poor chunks are the most common type of chunk and can be found in all strata where ores are available. A poor regular chunk will offer 3 nuggets and a poor crystalized chunk will offer 6 nuggets.
- Medium chunks, like poor chunks, can be found in all strata where ores are available. A medium regular chunk will offer 4 nuggets and a medium crystalized chunk will offer 8 nuggets.
- Rich chunks are somewhat uncommon and can be found in less strata than poor and medium chunks. A rich regular chunk will offer 5 nuggets and a rich crystalized chunk will offer 10 nuggets.
- Bountiful chunks are also uncommon and in strata where they are accessible, it is more likely that one will find greater amounts of rich ore than bountiful ore. A bountiful regular chunk will offer 7 nuggets and a bountiful crystalized chunk will offer 14 nuggets
Smelting metal
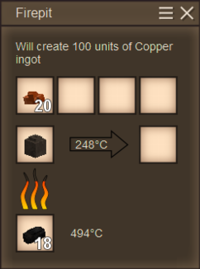
The first step to processing metal is smelting, which is performed in a crucible. A single crucible can hold up to four complete stacks of 128 nuggets, however only one pure metal or alloy may be smelted within the crucible at a time. Each nugget is equivalent to 5 units of metal, which means that a full crucible can hold up to the equivalent of 2560 units. Most tools or ingots require 100 units (20 nuggets) per mold, with the exception of a few larger items, such as plates, anvils, and metal blocks, which can require significantly more.
Nugget ratios that do not fulfill this numeric requirement create amounts of metal too small to cast.
Pure metal smelting is very simple in that the same nugget type can be used throughout the entire process. Alloy smelting is slightly more complicated, as the ratios of each alloy all differ and the appropriate mix of several kinds of nuggets must be placed in the crucible prior to heating.
The number of nuggets that can be used for an alloy are somewhat variable, which can be advantageous if certain nuggets are in shorter supply. As an example, an alloy of Bismuth Bronze requires 10 to 20% bismuth, 50 to 70% copper, and 20 to 30% zinc or, broken down into nuggets, 2 - 4 bismuth nuggets, 10 - 14 copper nuggets, and 4 - 6 zinc nuggets.
If more zinc is available, a ratio of 2 bismuth nuggets, 12 copper nuggets, and 6 zinc nuggets can suffice, and vice versa, if more bismuth is available, a ratio of 4 bismuth nuggets, 12 copper nuggets, and 4 zinc nuggets is acceptable.
Preparing the crucible
- Place the crucible in the input slot (left) of the firepit to access the crucible GUI
- Add nuggets into one or more of the four input slots of the crucible GUI.
- When a proper alloy ratio has been reached, the GUI will display the amount in metal units and either the pure metal or alloy that will be produced from the smelting process.
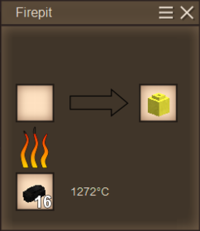
- Add fuel and light the fire pit. Selecting the appropriate fuel is paramount to raising and maintaining the temperature of the metal above its particular smelting temperature, which liquifies the nuggets.
- When the nuggets have been fully liquified, the glowing crucible will shift to the output slot (right) of the firepit. The crucible will begin to cool down if it remains in the output slot or is otherwise pulled away from the heat, and if the crucible cools down far enough without being casted, the liquefied metal will be rendered solid and be otherwise unusable until heated up again.
Adding or removing ores after the process has begun will reset the temperature.
Casting metal
Once smelted, liquified metal is available within a crucible, it is ready to be cast within ingot or tool molds.
Filling molds
- Place the required mold to be filled on a solid surface. Tool molds occupy one block while ingot molds may be placed two to a block.
- With the glowing crucible in an empty hand (active hotbar slot) and a pair of tongs in your off-hand, select the desired mold with the display crosshairs and pour the liquid metal into that mold.
- When the mold is filled, metal will no longer be allowed to be added into the mold.
- The metal will reach various states of cooling in the mold- from liquid to soft to hardened to cold - which can be identified with the current item temperature in the mold GUI.
- When the tool or ingot is hardened or completely cold, it can be removed from the mold.
If a mold is picked up before the metal is hardened or cold, the soft or liquid material will be lost. Subsequently, a partially filled mold cannot be picked up, even if the metal is cold, because there are no assets available for metals that are too small to be fully cast and utilized.

|
Protip:
Liquid metal of two different types cannot be added to a mold to get an alloy. Pure metals and alloys must be heated and liquified within the crucible before being poured. |
Mold availability
| Mold | Mold Type | Tool Type | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Anvil | Crafting | Manual and mechanized smithing. |

|
Axe | Harvesting | Chopping leaf, plant, and wood blocks, including trees, logs, planks, fences, gates, and other wooden building components; creates firewood. |

|
Falx blade | Combat | Mob damage, melee combat weapon. |
|
Hammer | Crafting | Crushing ores, crystal clusters, and certain soft stones; crafting components for mechanical power, item transportation, and steel carburization; polishing stone; cutting stone brick. |

|
Helvehammer | Crafting | Mechanized smithing. |

|
Hoe | Crafting | Tilling and converting soil for farming. |

|
Ingot | Crafting | Ingot distribution, which can be used for manual and mechanized smithing and crafting components. |

|
Lamallae | Combat | Creating and repairing body lamellar armor. |

|
Pickaxe | Harvesting | Mining ceramic, rock, stone, ore, metal, and ice blocks. |
|
Prospecting Pick | Harvesting | Damaging rock blocks for long and short range ore and mineral detection. |
|
Shovel | Harvesting | Digging clay, gravel, peat, sand, soil, and snow blocks. |
Metal Types
There are 27 types of metal available for collection and usage, 14 castable metals and 13 uncastable metals. Of those castable metals, 6 are tiered, or tied to progression through the metallurgic ages, and 8 are untiered, which while useful, do not contribute to any advancement on their own merits.
Castable Metals
| Ingot | Nugget | Bits | Metal | Geologic Name | Metal Type | Tier | Alloy% | % Conversion in nuggets |
Smelting Temperature | Casting Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|

|
Copper | Native copper Malachite |
Pure | 2 | ❌ | ❌ | 1084°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |

|

|

|
Gold | Native gold | Pure | 2 | ❌ | ❌ | 1063°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |

|

|

|
Silver | Native silver | Pure | 2 | ❌ | ❌ | 961°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |

|
❌ | 
|
Tin Bronze | ❌ | Alloy | 3 | Copper: 88 - 92% Tin: 8 - 12% |
Copper: 18 Tin: 2 |
950°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |

|
❌ | 
|
Bismuth Bronze | ❌ | Alloy | 3 | Bismuth: 10 - 20% Copper: 50 - 70% Zinc: 20 - 30% |
Bismuth: 2 - 4 Copper: 10 - 14 Zinc: 4 - 6 |
850°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |

|
❌ | 
|
Black Bronze | ❌ | Alloy | 3 | Copper: 68 - 84% Gold: 8 -16% Silver: 8 -16% |
Copper: 16 Gold: 2 Silver: 2 |
1020°C | Armor, ingots, tools, weapons, nails and strips |
| Ingot | Nugget | Bits | Metal | Geologic Name | Metal Type | Tier | Alloy% | % Conversion in nuggets |
Smelting Temperature | Casting Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Bismuth | Bismuthinite | Pure | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 271°C | Ingots |

|

|
|
Lead | Galena | Pure | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 327°C | Ingots, leaded glass panes |

|

|

|
Tin | Cassiterite | Pure | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 232°C | Ingots |

|

|

|
Zinc | Sphalerite | Pure | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 419°C | Ingots |

|
❌ | 
|
Brass | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Copper: 60 - 70% Zinc: 30 - 40% |
Copper: 12 - 14 Zinc: 6 - 8 |
327°C | Ingots |

|
❌ | 
|
Lead Solder | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Lead: 45 - 55% Tin: 45 - 55% |
Lead: 9 - 11 Tin: 9 - 11 |
327 °C | Alcohol distillation, ingots |

|
❌ | 
|
Molybdochalkos | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Copper: 8 - 12% Lead: 88 - 92% |
Copper: 2 Lead: 18 |
902 °C | Ingots |
|
❌ | 
|
Silver Solder | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Silver: 40 - 50% Tin: 50 - 60% |
Silver: 8 - 10 Tin: 10 - 12 |
758 °C | Alcohol distillation, ingots |

|
❌ | 
|
Electrum | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Gold: 40 - 60% Silver: 40 - 60% |
Gold: 8 - 12 Silver: 8 - 12 |
1010 °C | Rift Ward, Jonas assemblies, tools, ingots |

|
❌ | 
|
Cupronickel | ❌ | Alloy | ❌ | Copper: 65 - 75 % Nickel: 25 - 35% |
Copper: 13 - 15 Nickel: 5 - 7 |
1171 °C | Jonas assemblies, ingots, nails and strips |
Uncastable Metals
These metals can be found within the game’s asset library or in game, but cannot currently be smelted, cast, and/or worked.
| Ingot | Nugget | Bits | Metal | Geologic Name | Metal Type | Tier | Alloy% | % Conversion in nuggets |
Smelting Temperature | Casting Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
   
|

|
Iron | Hematite Limonite Magnetite |
Pure | 4 | ❌ | ❌ | 1482°C | ❌ |

|
|

|
Meteoric Iron | ❌ | Pure | 4 | ❌ | ❌ | 1476°C | ❌ |
 
|
❌ |  
|
Blister Steel Steel |
❌ | Pure | 5 | ❌ | ❌ | 1602°C 1502°C |
❌ |

|
|

|
Chromium | Chromite | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 1907°C | ❌ |
| ❌ | 
|
❌ | Manganese | Rhodochrosite | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |

|

|

|
Nickel | Pentlandite | Pure | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 1455 °C | ❌ |

|
❌ | 
|
Platinum | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 1770°C | ❌ |

|
❌ | 
|
Rhodium | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |

|
❌ | 
|
Stainless Steel | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |

|

|

|
Titanium | Ilmenite | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | 1668°C | ❌ |

|

|
|
Uranium | Uranium | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| ❌ | 
|
❌ | Tungsten | Wolframite | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Casting Tutorial Videos
| Ores, metals and minerals | |
|---|---|
| Guides | Ore Deposits • Metals |
| Metals | Copper • Iron • Meteoric iron • Gold • Silver • Lead • Tin • Zinc • Bismuth • Titanium (Ilmenite) • Nickel |
| Alloys | Bronze (Tin bronze, bismuth bronze, black bronze) • Steel • Brass • Solder (Lead solder, Silver solder) • Molybdochalkos • Cupronickel • Electrum |
| Minerals | Alum • Borax • Cinnabar • Coal • Halite (Salt) • Lapis lazuli • Quartz • Saltpeter • Sulfur • Sylvite (Potash) |
| Tools | Pickaxe • Hammer • Prospecting Pick • Crucible • Forge • Ore blasting bomb • Quern • Anvil • Bloomery • Helve hammer • Pulverizer |
| Other | Gemstones |
| Related mechanics | Panning • Mining • Clay forming • Casting • Smithing • Steel making |
| Wiki Navigation | |
|---|---|
| Vintage Story | Guides • Frequently Asked Questions • Soundtrack • Versions • Controls |
| Game systems | Crafting • Knapping • Clay forming • Smithing • Cooking • Temperature • Hunger • Mining • Temporal stability • Mechanical power • Trading • Farming • Animal husbandry |
| World | World generation • Biomes • Weather • Temporal storms |
| Items | Tools • Weapons • Armor • Clothing • Bags • Materials • Food |
| Blocks | Terrain • Plants • Decorative • Lighting • Functional • Ore |
| Entities | Hostile entities • Animals • NPCs • Players |
| Miscellaneous | List of client commands • List of server commands • Creative Starter Guide • Bot System • WorldEdit • Cinematic Camera • Adjustable FPS Video Recording • ServerBlockTicking |